Why is blood sugar balance important?
How does continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) help healthy people maintain blood sugar balance?
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the body’s main source of energy. Every time we consume carbohydrate-rich food, it is broken down into glucose, which is absorbed into the bloodstream and provides energy to the brain, muscles, and other tissues.
However, large fluctuations in blood sugar—too high or too low—can cause health problems both in the short and long term.
The role of blood sugar in fueling the body
- Brain function – The brain primarily uses glucose, making blood sugar balance important for concentration and memory.
- Muscle performance – Glucose is an essential energy source for physical activity and endurance.
- Supplying cells with energy – Glucose is necessary for vital daily functions, such as digestion and immune system activity.
When blood sugar is stable, we feel energetic, focused, and balanced. When it fluctuates sharply, it can cause fatigue, brain fog, and strong cravings.
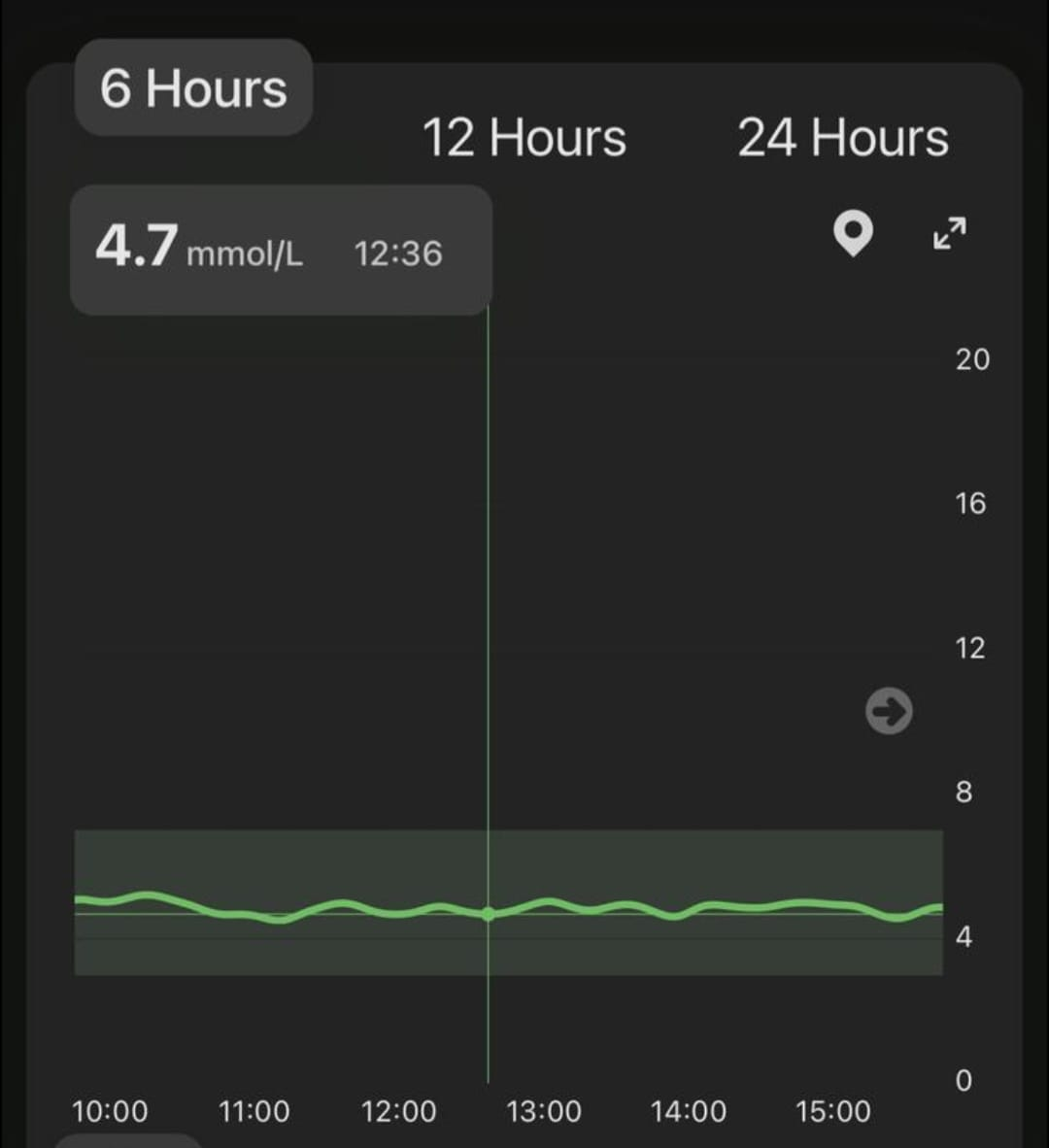
How does blood sugar balance affect well-being?
Mood and mental well-being
- High blood sugar can cause anxiety, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
- Low blood sugar can cause nervousness, dizziness, and even bursts of anger or irritability.
- Stable blood sugar helps maintain a calm and balanced mood.
Sleep and recovery
- Large blood sugar fluctuations before bedtime can disturb sleep and cause nighttime awakenings.
- If blood sugar drops too low at night, stress hormones may be activated, making sleep restless.
Concentration and energy
- When blood sugar drops sharply after a spike, fatigue and brain fog may occur.
- Stable blood sugar helps maintain clear thinking and steady energy levels throughout the day.
Why should a healthy person monitor blood sugar?
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) helps understand how different foods and lifestyle choices affect blood sugar balance. Stable blood sugar improves both physical and mental well-being, reduces cravings, and helps prevent metabolic issues.
If you want more energy, better sleep, and stable mood, it’s worth monitoring blood sugar fluctuations consciously!
What are healthy blood sugar ranges?
- Fasting blood sugar: 4.0–4.7 mmol/L.
- Average daily blood sugar: 4.4–5.6 mmol/L.
- Blood sugar 2 hours after eating: no higher than 7.8 mmol/L.
What are glucose spikes and why avoid them?
A glucose spike is a sharp rise in blood sugar after eating, mainly caused by carbohydrate-rich foods. When you consume food that breaks down quickly into glucose (e.g., bread, sweets, fruit juices), sugar enters the bloodstream rapidly, raising blood sugar levels very high in a short time.
Why are glucose spikes a problem?
- Fatigue – drowsiness and energy loss occur after meals.
- Cravings – especially for sugary and carb-heavy foods.
- Concentration difficulties – blood sugar fluctuations affect brain activity, causing brain fog.
Long-term impact on health
When glucose spikes occur frequently, they affect metabolism and insulin function:
- Insulin resistance – cells become less sensitive to insulin, which may lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Fat storage – excess insulin promotes fat storage, especially in the abdominal area.
- Inflammation and oxidative stress – blood sugar fluctuations may trigger chronic inflammation in the body.
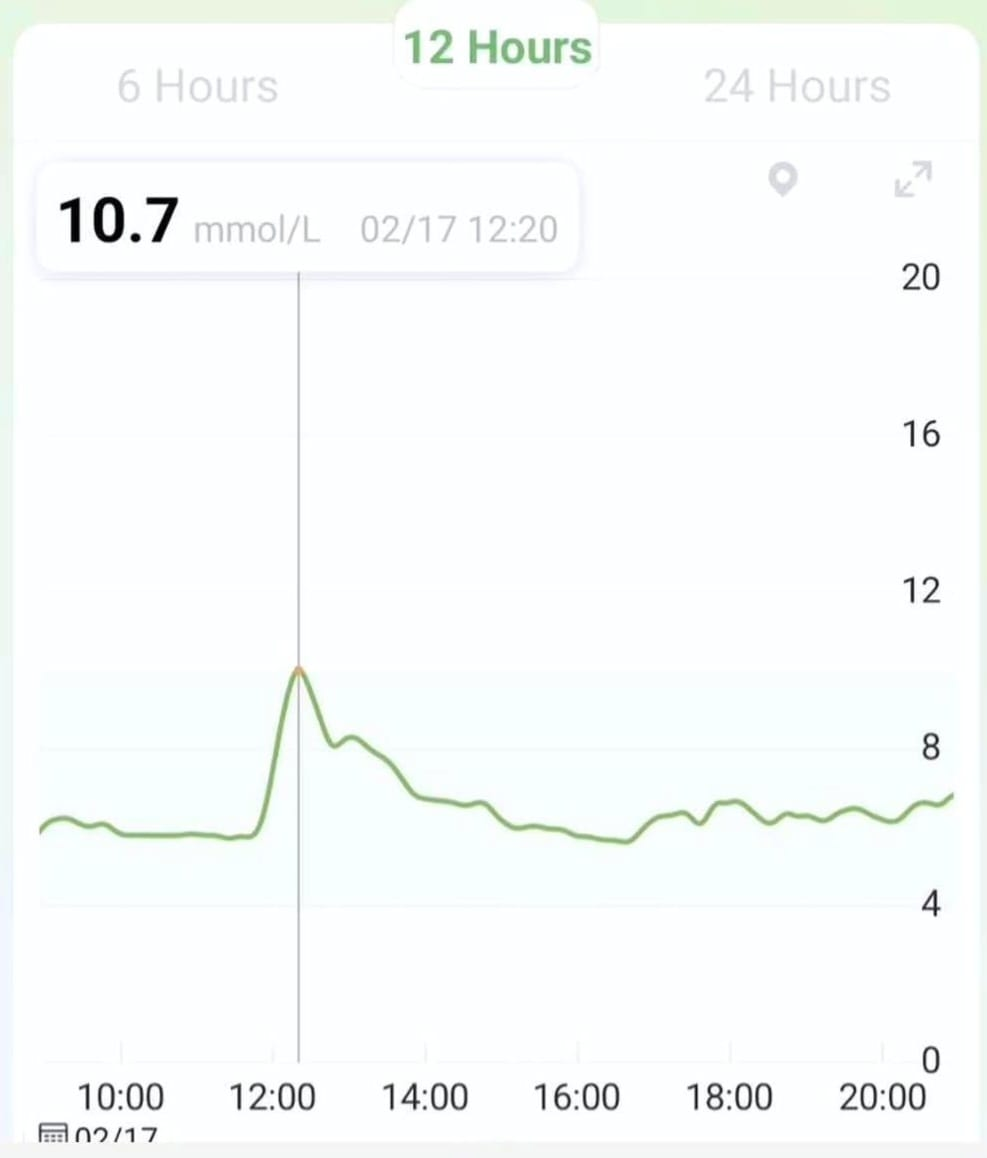
Foods that cause glucose spikes
Not all carbohydrates are equal. High glycemic load foods tend to raise blood sugar faster and higher.
Highest-risk foods:
- White bread, pastries, and croissants
- Rice, pasta, and potatoes (especially without added fiber)
- Breakfast cereals and granola bars
- Porridge (especially without added fiber)
- Fruit juices and soft drinks
- Candies, cookies, and chocolates
- Foods made with sugar and flour
Alternatives to avoid glucose spikes:
- Proteins and fats – add them to each meal (e.g., eggs, nuts, avocado, olive oil).
- Fiber-rich foods – whole grains, legumes, and leafy greens slow glucose absorption.
- Correct eating order – eat proteins and fats before carbohydrates to prevent sharp blood sugar spikes.
How does CGM help improve health long-term?
- Helps identify the most suitable diet for each individual.
- Improves metabolic flexibility.
- Stabilizes weight and reduces cravings.
- Helps prevent diabetes and insulin resistance.
By monitoring blood sugar balance with continuous glucose monitoring, you can improve your quality of life and prevent health problems before they arise!
Get your glucose monitor conveniently from our online store.